Financial advisors, accountants, and bookkeeping industry professionals are increasingly acting as virtual Chief Financial Officers (CFOs). This is not surprising—as game-changing software has opened opportunities for bookkeepers to expand upon traditional offerings, many are perfectly poised to act as virtual CFOs for their clients.
So, what exactly are virtual CFO services? How do businesses benefit from them? And how might you best deliver them? Let’s dig in!
What is a CFO?
Firstly, let’s look at what a CFO does. A CFO or chief financial officer is a role usually reserved for larger organisations or companies that require incise financial oversight and management. CFOs are primarily responsible for the financial actions, health, and trajectory of an organisation.
While many smaller businesses tend to the manage financial health of their company themselves, or within smaller roles, more complex businesses (often focused on fierce growth) hire a CFO.
A CFO’s responsibilities can include:
- Tracking cash flow.
- Diagnosing financial strengths and weaknesses.
- Laying a path to financial stability and success.
- Conducting risk assessments.
- Financial insight, planning, and forecasting.
- Investment strategy.
- Fundraising and capital management.
- Complex reporting.
- Compliance.
- Managing a team.
What is a virtual CFO and how do they function?
A virtual CFO, on the other hand, essentially provides a reduced CFO service remotely. As such, virtual CFOs are often engaged by smaller entities that require basic ‘chief financial officer’ facilities but not to the extent of needing to hire or engage a traditional CFO figure.
While traditional CFOs demand high salaries (and their talents are best spent on large and complex companies, often with a sizeable team beneath them) smaller businesses can also reap enormous benefits from some level of support. This is the perfect niche for a virtual CFO service.
The beauty of a virtual CFO is that a business can hire a remotely-based business advisor on a part-time basis to perform the basic functions of the role but without the high expense!
What are the various virtual CFO services you can provide?
So, what kind of work can you offer your client as a virtual CFO? As a virtual CFO, you’ll only be working remotely on a part-time or contract basis, which, of course, leaves you open to other work and the ability to juggle multiple clients.
In your part-time capacity, you’ll need to discuss the specific needs of each client, as they can vary wildly. Depending on the client you can offer a mixed bag of the following services:
- reporting and insights
- business lifecycle advice
- assistance in making better business decisions
- financial management
- cloud software-based oversight
- budgeting and forecasting
- maintaining accounting records
- improving profitability
- cash flow projections
- growth planning
- risk assessment
- back-office functions
- cloud accounting
- raising capital.
There are also a range of similar services you could offer as well, depending on your client and your abilities and areas of knowledge.
How do you become a virtual CFO?
To become a virtual CFO, you’re going to need knowledge, education, and financial expertise.
Furthermore, a strong track record of experience and a solid client base is also helpful. However, for someone already in the bookkeeping or accounting industry, this is an entirely achievable goal. The foundations have already been laid. You can start by upselling your existing customers to get things rolling.
If you have an advisory background, offer consulting services, and have the requisite skills to offer CFO services, you can confidently start offering yourself as a virtual CFO right away, or get the ball rolling by upskilling with additional finance-related education. The latter will always be seen favourably by your client base.
You’ll also have to make a shift in your marketing, including your branding and website, so you convey that you’re more than just a process-focused bookkeeper. Creating thought leadership content and having your first client onboard to give your virtual CFO skills a testimonial is also advisable.
On top of the hard skills, to best engage clients as a virtual CFO, you’ll also need to be completely cloud-based and highly proficient in a wide range of software tools, especially accounting. You’ll be remote after all, so technological ability and comfortability in the cloud is a must.
What benefits do businesses receive from engaging with a virtual CFO?
Of course, most small businesses don’t need (or can’t afford!) a CFO. However, there are stacks of potential clients who need more than tax or compliance bookkeeping services, whether regularly or leading up to the end of the financial year. Indeed, many business owners want to make better business decisions, master cloud accounting, raise capital, become more stable, or better understand the minutia of their financial performance.
As a bookkeeper, it’s likely you already offer advisory or business consulting services, so offering tailor-made virtual CFO services is not a gigantic leap, although it sounds rather lofty!
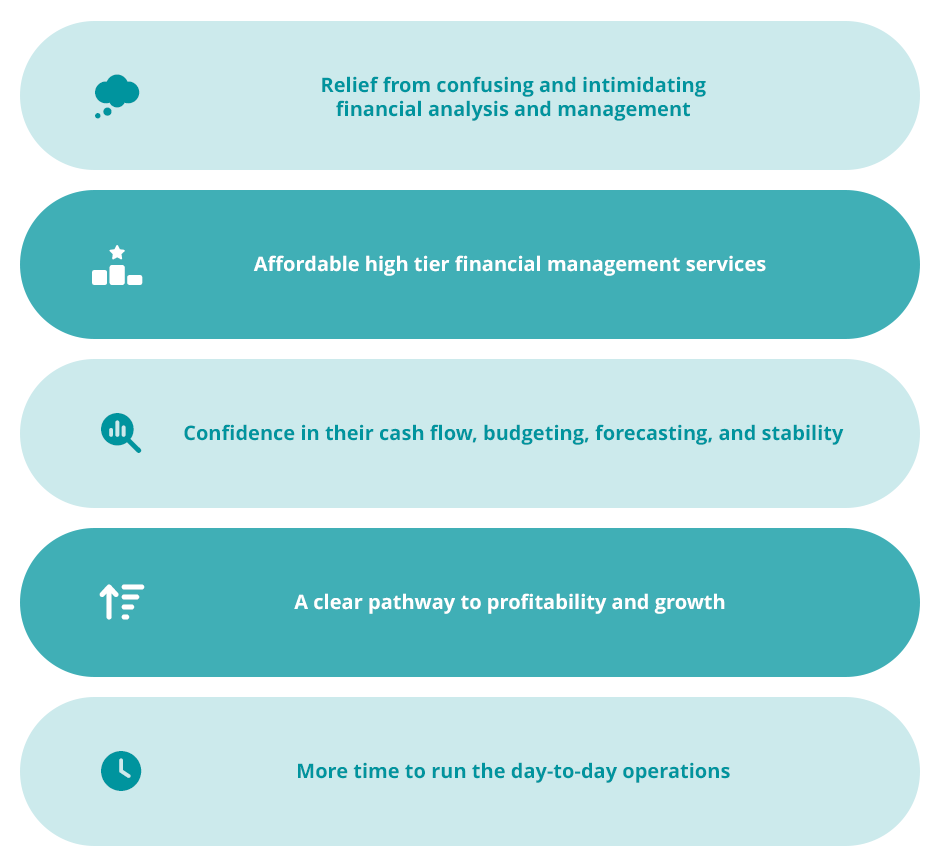
Engaging a virtual CFO, small businesses will receive:
- Relief from confusing and intimidating financial analysis and management.
- Affordable high-tier financial management services.
- Confidence in their cash flow, budgeting, forecasting, and stability.
- A clear pathway to profitability and growth.
- More time to run the day-to-day operations.
By engaging a virtual professional, businesses can enjoy the tangible advantages of a traditional CFO, but without high costs, and all handled remotely at a service level that suits them, businesses are waking up to virtual CFO services. It’s up to you to capitalise on these needs and offer real value.

